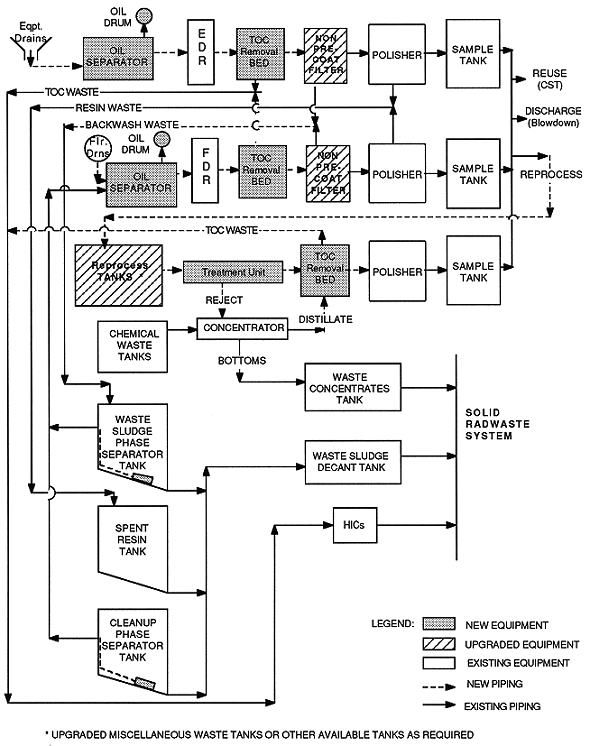
Fig. 1. Recommended Laguna Verde
liquid radwaste processing flow chart.
Ing. Alejandro Garcia Martinez
Comision Federal de
Electricidad
Larry Campo, Donald Gardner, Craig Knauss, and Edward Taylor
Raytheon Nuclear Company
ABSTRACT
The Comision Federal de Electricidad (CFE) performed a review of the existing Laguna Verde Nuclear Plant (LVNP) liquid radwaste system design and operational performance. Radwaste streams were identified and characterized. Processing protocols used by the operations staff were reviewed and compared against current industry protocols. The review determined that the amount of liquid radwaste generated was substantially above the Plant's designed basis.
It was determined that programmatic and engineering enhancements to the existing liquid radwaste generation, collection and treatment program process could be achieved, reducing the amount of waste generated and processed to acceptable levels.
Figure 1 depicts the Laguna Verde liquid radwaste process flow. Recommended new equipment, recommended upgraded equipment, existing equipment, and associated new and existing piping are featured.
CONCLUSIONS
The review concluded that the existing LVNP liquid radwaste management program was adequate to meet station operational objectives assuming programmatic and engineering adjustments are implemented. These adjustments are being implemented and are beginning to reduce liquid inputs into the radwaste system. Other benefits expected are:
In all, several liquid radwaste programmatic and engineering upgrades were identified. The upgrades, projected benefits, and cost pay back of upgrade implementation were evaluated to ensure that CFE's operating objectives are met at minimal operational costs.

Fig. 1. Recommended Laguna Verde
liquid radwaste processing flow chart.
INTRODUCTION
The Laguna Verde Nuclear Plant (LVNP) is located in the area known as "Laguna Verde" which is south of the town of Palma Sola and some 70 kilometers north of Vera Cruz City in the state of Vera Cruz, Mexico. Surface access to the site is by the Tuxpan-Puerto Juarez Highway (Mex. 180), Villa Cardel-Nautla Section. An access road, approximately 2 kilometers long connects the site to the above mentioned highway at Kilometer 44.5.
The Plant consists of 2 units, each unit consisting of a boiling water type reactor and a tandem compound quadruple flow turbine. The turbine-generator units each have a nominal capacity of 674,480 kW at 1800 rpm when supplied with saturated steam at 970 psia. Cooling water for the condensers is taken from the Gulf of Mexico. Unit 1 and Unit 2 began operation July 1990 and April, 1995, respectively.
Liquid radioactive waste generation, collection, processing and storage management are key issues to the success of the Radioactive Waste Program at LVNP. In early 1995, the Comision Federal de Electricidad (CFE) performed an evaluation of the Liquid Radwaste Program at LVNP. The results of the initial liquid radwaste program evaluation lead to the overall project of providing programmatic and engineering upgrades for the LVNP liquid radwaste system. The goal of the Liquid Programmatic and Engineering Upgrades Project is to provide a cost effective and ALARA liquid radioactive waste program for LVNP. A secondary goal of the project was to utilize the existing liquid radwaste processing equipment to the greatest extent practicable in any equipment upgrade process.
The Liquid Programmatic and Engineering Upgrades Project was performed in three basic steps as follows:
An overview of these project steps is provided as follows:
STEP 1 - EVALUATION OF THE EXISTING LIQUID RADWASTE PROGRAM, RECOMMENDATIONS IDENTIFICATION, AND COST VERSES BENEFIT ASSESSMENT
Program Evaluation and Recommendations Identification
The evaluation of the existing liquid radwaste program was performed during the first and second quarters, 1995. For evaluation purposes, LVNP FSAR liquid radwaste volume generation projections was used as the design basis and compared against to the actual liquid waste generation rate at the Plant. Additionally, Nuclear Plant comparison information was obtained from the Institute for Nuclear Power Operation's Nuclear Network. (See Table I)
Table I The Specific Liquid Radwaste Systems Evaluated and
Evaluation Parameters
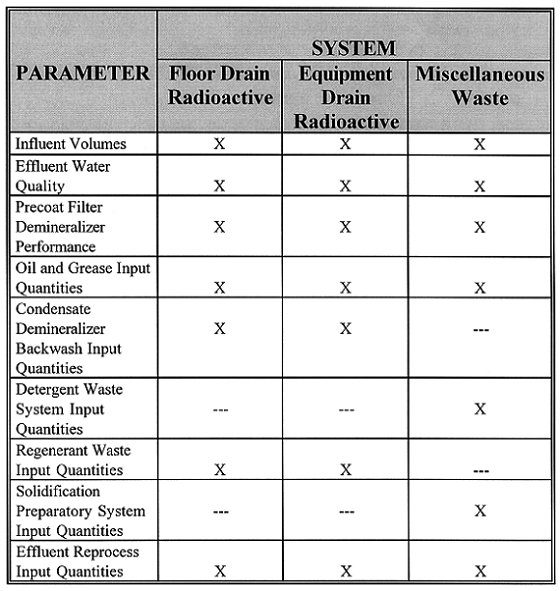
The evaluation showed that the actual generation of liquid radwaste had exceeded the design basis by 41%. The reasons for the increased generation were identified and conclusions reached. Recommendations were developed to reduce the quantity of liquid waste generated, with the design basis as the target. The liquid radwaste generation rate projected (assuming that all recommendations were implemented) was 67% of the design basis and 47% of the actual liquid radwaste generation rates. In all, 12 programmatic and 10 engineering recommendations were provided. The engineering recommendations all focused on adding equipment enhancements to existing equipment. The programmatic recommendations focused on utilizing industry proven liquid radwaste management solutions. (See Table II)
Table II An Overview the Engineering and Programmatic
Recommendations and Projected Benefits
Engineering Recommendations
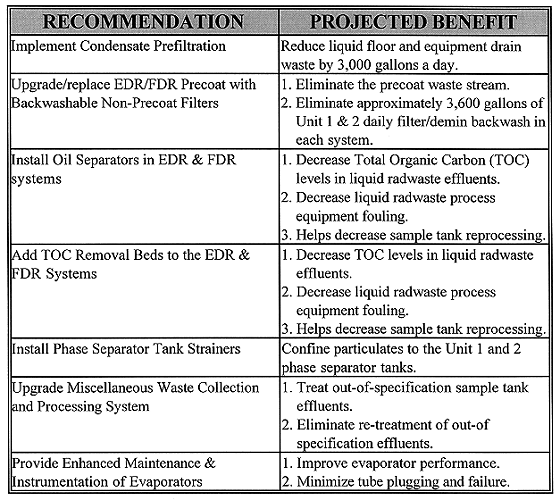
Table III Programmatic Recommendations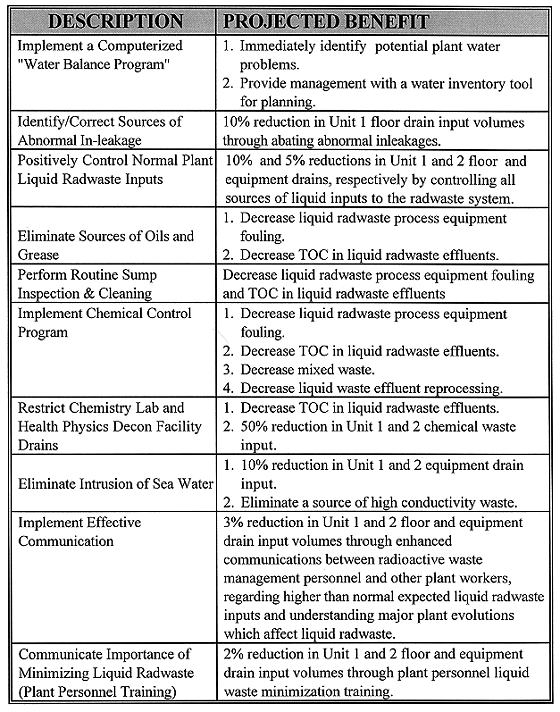
Cost Versus Benefit Assessment of the Recommendations
A cost verses benefit evaluation was performed to ascertain whether the liquid radwaste programmatic and engineering recommendations were viable from a financial perspective. For the cost verses benefit assessment of liquid radioactive waste recommendations, the following cost parameters were considered:
Costs associated with the above items were develop for the conceptual case - implementing all liquid radioactive waste recommendations and the base case - current liquid radioactive waste system. The operations and maintenance costs of each were then compared and savings associated with the recommendation signified. The savings identified were then compared to the total installed cost of the recommended upgrades and a payback period was determined. All costs, except for capital costs were reported on an annualized basis in 1994 US dollars. Capital costs were reported in 1994 US dollars.
The cost versus benefit assessment performed identified a payback period of slightly over one year, after all recommendations were implemented.
STEP 2 - RECOMMENDATION DEVELOPMENT
Recommendation development began in the third quarter, 1995 and is expected to be completed in early 1998. For the Liquid Radioactive Waste Programmatic and Engineering Upgrades Project, the recommendations that were to be developed were subdivided into three work activity groups, 1) Program Development, 2) Methodology Guidelines Development, and 3) Design Engineering. All work activities were performed in a team approach consisting of Raytheon performing first stage program and methodology development and engineering conceptual and preliminary designs. CFE performed final program and methodology development as well as final design engineering.
The CFE/Raytheon teaming approach for this Project was very advantageous for the following reasons:
STEP 3 - RECOMMENDATION IMPLEMENTATION STATUS
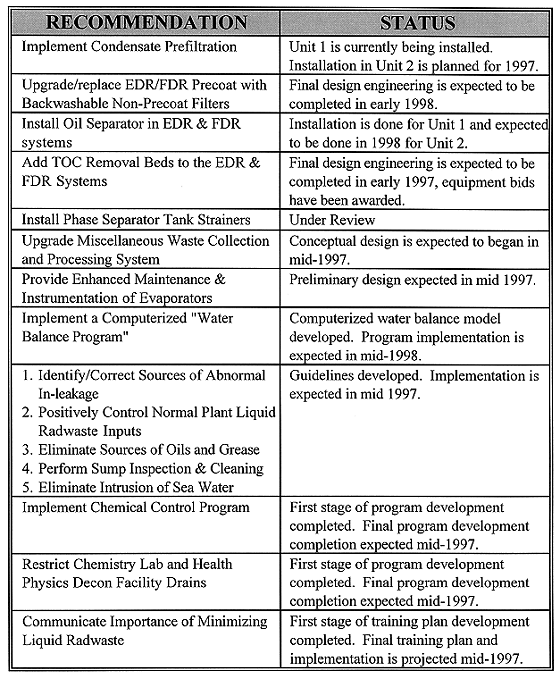
The implementation status of each recommendation is presented in Table IV. Implementation of all recommendations is expected prior to the end of 1997.
Table IV Implementation Staus of Each Recommendation
CONCLUSION
The Comision Federal de Electricidad and Raytheon Engineers & Constructors evaluated the performance of the liquid radwaste system at the Laguna Verde Nuclear Plant. The evaluation produced 21 recommendations for improvement. The recommendations projected that the volume of liquid radwaste generated could be reduced by 47% with a capital cost payback period of approximately one year. All of the recommendations have been developed into work packages and have received preliminary work activities. One of the recommendations have been fully implemented and the volume of liquid radwaste generated is being reduced. Other recommendations are currently being implemented.