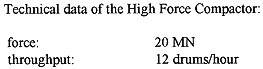
W. Stich
NUKEM GmbH
63755 Alzenau
Germany
M. Köver
SE-VYZ Slovenské elektrárne,
A.S.
91931 Jaslovske Bohunice
Slovakia
ABSTRACT
The nuclear power plants in the eastern European countries and in the states of the former USSR are today faced with significant waste problems. In the Republic of Slovakia, for example, with 2 operating VVER reactors at the site of Bohunice - V1 and V2 - and 2 more under construction at Mochovce, the systematic and safe disposal of nuclear waste is generally not solved.
Some promising concepts, facilities for treatment of liquid waste, are not in operation today. Bitumization in 200 liter drums, the chosen method, is actually not accepted as a waste container for final storage.
An additional problem exists at the site of Bohunice from the disabled reactor A1, where same reactor fuel and a large amount of liquid and solid waste, with unusual physical and chemical properties as well as activity, is stored under unacceptable conditions.
In 1992, the Slovak utility SE (Slovenské Elektrárne) decided to realize the Waste Treatment Center (BSC-RAO) at Bohunice in order to avoid the threatened shut-down of the nuclear plants due to overfilling available waste storage capacity and also to solve the A1 problem. NUKEM was the selected contractor for design and construction of the waste treatment facilities.
DESIGN
The Waste Treatment Center of Bohunice is designed to treat and condition to a form suitable for final disposal wastes accumulated to date as well as arising from future operation of the Bohunice and Mochovce NPP´s and other sources. Wastes handled include solid LLW and liquid LLW and MLW. The conditioned products, filled concrete containers under licence from French SGN, are in accordance with the requirements for final disposal.
The waste to be treated in the Waste Treatment Center is divided into the following categories:
Based on this classification and the requirements for final disposal in Slovakia the following equipment is installed:
All necessary auxiliary systems for media and electrical supply are included. Additionally the center will be furnished with:
DESCRIPTION OF THE EQUIPMENT INSTALLED IN THE CENTER
Transport and Storage of the Waste
Solid waste is transported within 20' containers or 200-liter drums using lorries to the reception depot of the Waste Treatment Center. The lorries are unloaded using a special transport vehicle and prepared for distribution to the treatment facilities.
Liquid waste is transported to the Waste Treatment Center in a special mobil tank or pumped to the feed vessel of the liquid waste treatment facility.
Sorting Facility
If possible, the solid waste will be pre-sorted at the place of origin and transported in 200-liter drums from the reception depot to the sorting room for controlled sorting and dismantling of bigger pieces. Here the waste is passed over a sorting table, unwrapped and conveyed into the sorting box.
The waste is sorted according to the following criteria:
The compactable waste will be placed to a 200-liter drum docked to the sorting box. For a better utilization of the drum volume equipment for size reduction of larger pieces such as hacksaw, metal scissors and circular saw are provided in the sorting box. The filled drums will be closed by means of a lid and transported to the high-force compactor.
Decontaminable waste will be collected in a carriage lined with film, which also is docked to the sorting box, and later on transported to a decontamination site outside of the Waste Treatment Center.
In the sorting box, the combustible waste will be wrapped in plastic bags or paper bags and placed in a 200-liter drum for transport to the incineration plant.
Compaction
In the compaction plant, the sorted waste contained in 200-liter drums will be compacted by means of a high force compactor. The compacting room is designed as a first barrier to avoid the spread of contamination. During the compacting of 200-liter drums, the high force compactor is additionally closed by means of integrated lifting bulkheads. Any dust generates will be extracted.
After presorting ( height, weight ) of the compacted 200-liter drums ( pellets ) they will be placed in a 3 m3 concrete container and transport to the cementation plant for filling of the voids between the compacted waste pellets and the concrete container.
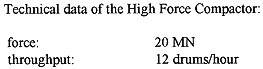
Superconcentration
In the concentration plant, the radioactive concentrates are further concentrated to such an extent, that they can be solidified by cementation.
In the concentration, the following process steps are performed:
The final concentrate is pumpable and will be transferred to the cementation plant.
The separation the vapors from the evaporator takes place in a cyclone separator with subsequent condensation in the evaporator condenser.
Technical data of the evaporation plant:

Incineration
The gross composition of the solid waste to be burned is:

The solid waste is delivered in 200 liter drums. The drum is emptied by a lifting and tilting device into glove box. In this glove box the waste bags are manually transferred into the feeding box from where they are automatically fed into the incinerator.
In the incinerator the solid waste - more or less continuously conveyed - will be incinerated under sub-stoichiometrical conditions at a temperature of 900-1050°C. In the burning zone the waste will be transformed with air and steam into gaseous carbon hydrides, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and soot. This flue gas mixture will then be transported, together with the soot and unburnt particles, into the afterburner-chamber.
The liquid combustible waste will be homogenized in the mixer tank and pumped into the heating burner of the incinerator. In the afterburner-chamber the fluegas will be completely incinerated at a temperature of 1000-1150°C by the input of fuel. The oxygen concentration is controlled and maintained to at least 6 Vol% ( EC-Regulation). The residence time of the flue gas is more than two seconds. This assures the destruction of all organic compounds. In the upper part of the afterburner-chamber the fluegas is cooled down to 850°C by water injection.
The flue gas from the afterburner chamber will be cooled by adding air in a static mixer to 350°C. The following two reverse jet scrubbers remove harmful substances such as HCl and SO2. The pH-value of the scrubbing solution in the first scrubber is maintained between 0.5 and 1.5 and in the second scrubber between 7 and 9 by addition of caustic soda. If the salt concentration in the scrubber solution reaches at 10 - 15 weight per cent, it will be pumped batchwise via pipes into the cementation plant.
The off-gas leaving the reverse jet scrubbers is satured by water vapor and - for the purpose of avoiding condensation in the following parts of the plant - it will be heated up to about 30°C higher than the dew point. After that the off-gas passes HEPA-filters, were solid particles are retained with an efficiency higher than 99.996%. This particle filter forms the last barrier for the non-volatile radionuclides.
The two blowers after the HEPA-filters generate the low negative pressure which is necessary during operation. The main blower holds the negative pressure during the normal operation. The smaller blower is used during any interruption of the incineration process or in stand by mode.
The residues of combustion ashes and non-combustible material accumulated in the incinerator and in the afterburner chamber will be discharged via ash discharge boxes into a connected 200-liter drum via a double lid system and conveyed to the cementation plant.
Technical data of the Incineration plant:

Cementation
The cementation process is the last step in the creation of the final disposal product. The following waste is treated by means of cementation:
The homogeneous mixture of waste and cement will be poured into the 3 m3 concrete containers where it then cures.
The cementation of the waste comprises the following essential process steps:
Technical data of the Cementation plant:
| type of mixer: | inclined mixer |
| throughput charge: | 500 litre |
| mode of operation: | discontinous 24 hours/day 200 days/year |
| cement product: | about 14,000 kg/day |
| content of dried solieds in the final product: | up to 35% by weight |
State of the Project
The detail engineering for all treatment plants is finished and the necessary components for the Waste Treatment Center procured and on the site.
The main structure of the building is now complete and the larger components such as incinerator, afterburner-chamber, scrubber and tanks are already installed in the building. The internal installation of the building has begun.
The functional test and the commissioning of the installed equipment are planned during 1997.